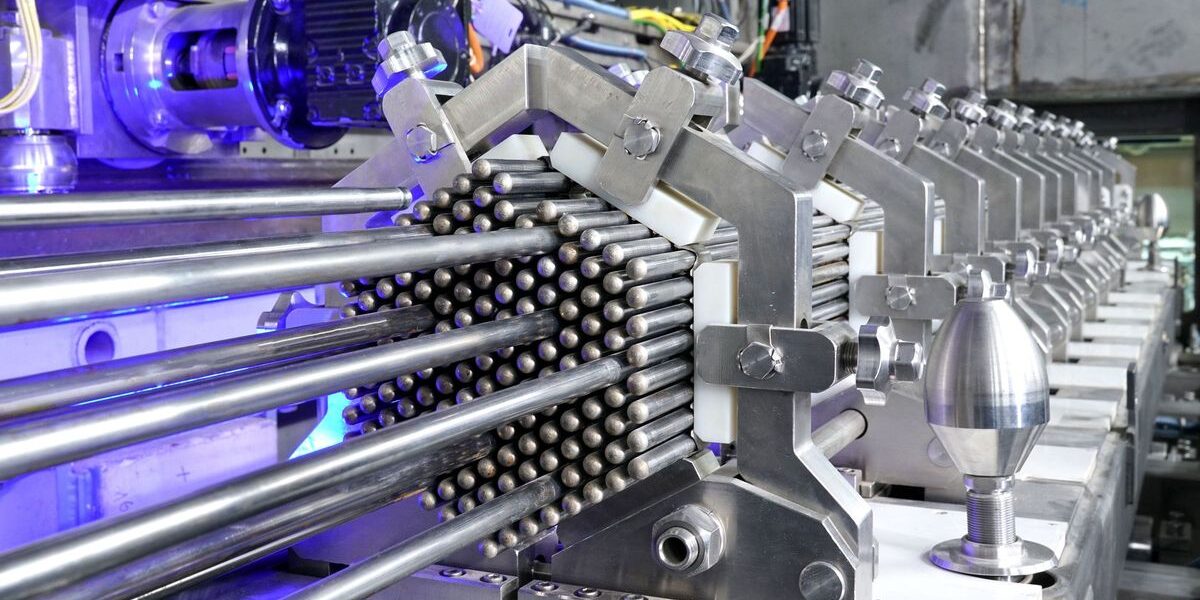
Rosatom achieved the first key milestone in the development of the Generation IV nuclear power system. The unit for fabrication/refabrication nuclear fuel for the innovative BREST-OD-300 fast neutron reactor was put into pilot operation in Seversk, Tomsk Region, West Siberia. It is the first of the three facilities of the unique Generation IV Pilot Demonstration Energy Complex (PDEC), which is under construction as part of the strategic project “Proryv” (of “the Breakthrough”) on site of the Siberian Chemical Combine (an enterprise of Rosatom's Fuel Division).
The cutting-edge fully automated facility has already successfully manufactured the first mockup fuel bundles of the BREST-OD-300 core design with depleted uranium nitride fuel pellets. All production sites of the new facility have undergone comprehensive testing.
The fuel fabrication facility includes four production sites: carbothermal synthesis of mixed uranium and plutonium nitrides, fabrication of fuel pellets, manufacturing of fuel elements, and assembly of complete fuel bundles. The staff personal of the facility will amount to 250 people.
Currently, the facility operators are mastering the technology and gaining experience in fabrication of BREST-OD-300 bundles with depleted uranium fuel matrix in compliance with the current license of Rostechnadzor (the Russian industrial and nuclear regulator). After the regulator approves handling of plutonium, the Siberian engineers will be able to start production of the target product – mixed dense nitride uranium-plutonium fuel (or the MNUP fuel), which would enable to fully implement all the advantages of Russian IV generation fuel, reactor and radiochemical technologies. Prior to the initial core loading of the BREST-OD-300, more than 200 of MNUP fuel bundles are scheduled for fabrication.
A unique technology for fabrication uranium-plutonium nitride fuel was developed in Russia by Rosatom scientists. The trial assemblies with experimental MNUP fuel elements were successfully tested in the BOR-60 fast research reactor, as well as in the commercial BN-600 fast reactor at the Beloyarsk NPP. The results of this irradiation and operation enabled to obtain data required for validation of the initial core loading of the BREST-OD-300, including the level of nuclear fuel burnup sufficient at this stage.
In total, the Pilot Demonstration Energy Complex will include three unique interconnected facilities: a unit for the manufacturing (fabrication/refabrication) of dense nitride uranium-plutonium nuclear fuel, a nuclear power plant with an innovative fast neutron lead-cooled reactor BREST-OD-300, and a unit for reprocessing of irradiated fuel. Thus, for the first time in the global practice, a NPP with a fast reactor and a stationary closed nuclear fuel cycle will be built on one site. After reprocessing, irradiated fuel will be sent for refabrication (i.e., re-manufacturing of fresh fuel). Thus, this system will become practically autonomous and independent of external supplies of energy resources.
“For this moment, Rosatom has the worlds furthest advancement the in development of Generation IV nuclear technologies. According to the IAEA classification, this implies higher efficiency in the use of fuel raw materials, increased safety standards for the operation of nuclear plants, as well as a significant reduction in the amount of nuclear waste generation. All these principles are fully consistent with the technological solutions adopted at the Pilot Demonstration Energy Complex, such as the fuel made of depleted uranium and plutonium, the BREST reactor facility based on the principles of natural safety, and the latest more efficient radiochemical technologies for irradiated fuel reprocessing,” commented Alexey Likhachev, CEO of Rosatom State Corporation.
Also, to ensure final fuel fabrication at the PDEC site in Seversk, new production sites were boult at various enterprises of the Rosatom Fuel Division. In particular, manufacturing of various metallic components of the fuel bundles for initial core loading, as well as for the BREST-OD-300 mock-ups, has been developed at the Chepetsk Mechanical Plant in Glazov (the Udmurt Republic), the Elemash Machine-building Plant in Elektrostal (Moscow region) and the Novosibirsk Chemical Concentrates Plant (West Siberia).
Reference
BREST-OD-300 will be the world's first lead cooled fact reactor, its architecture is based on the principles of so-called natural safety. The reactor's efficiency will also be ensured through the use of innovative MNUP fuel. It consists entirely of secondary products of the nuclear fuel cycle – depleted uranium and plutonium. Thus, its production and operation will enable to expand the resource base of the nuclear power industry many times over, to reprocess irradiated fuel assemblies in order to produce fresh fuel instead of storing them, and to radically reduce the generation volume of nuclear waste and its activity level.
Fast neutron reactors:
Thermal neutron reactors, which form the basis of modern nuclear power industry, use about 1 % of natural uranium, while the remaining 99 % is sent for temporary storage or disposed of as radioactive waste. The advantage of fast neutron reactors is their ability to efficiently utilize secondary products of the fuel cycle (in particular, plutonium) for power generation. At the same time, having a high reproduction rate, fast reactors can produce more potential fuel than they consume, as well as “after-burn” (i.e., utilize with energy production) highly active transuranic elements (minor actinides).
Generation IV power systems:
According to the classification adopted by the IAEA, Generation IV nuclear power systems involve the application of various technologies that are united by a common result – higher fuel utilization efficiency, increased safety, energy efficiency, reduction of spent nuclear fuel, etc.
Generation IV nuclear power systems are capable of radically changing the nuclear power industry, primarily due to a new level of safety, expansion of fuel nomenclature, and significant reduction of radioactive waste. Russia is one of the leaders in the development of Generation IV technologies: Beloyarsk NPP has started pre-project work on the construction of the BN-1200M power unit, while in Tomsk region, for the first time in the global practice, the NPP powered by the BREST-OD-300 lead-cooled reactor and a stationary closed nuclear fuel cycle are under construction at the same site.